1. Introduction to Light Cycles in Cannabis Cultivation
Light cycles are a fundamental aspect of cannabis cultivation, as they directly affect the growth and development of plants. Understanding how these cycles work is essential for any grower, whether beginner or experienced. Cannabis plants, like all plants, rely on light to perform photosynthesis, which is the process by which they convert light into energy.
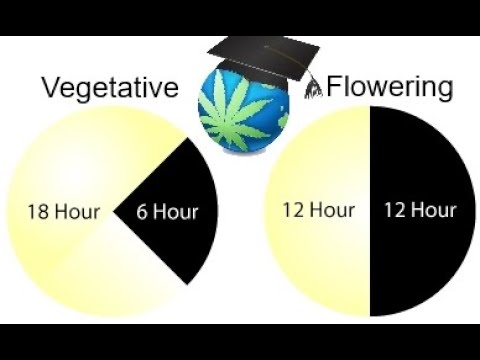
There are two main phases in the cannabis growing cycle: the vegetation phase and the flowering phase. During the vegetation phase, plants need around 18 to 24 hours of daily light. This promotes healthy growth and the development of robust leaves and branches. On the other hand, in the flowering phase, which usually starts when plants receive fewer hours of light (approximately 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness), flower production is activated, which is the main goal for most growers.
In addition, it is important to note that the type of light used also influences plant growth. LED, HPS (high-pressure sodium), and CFL (fluorescent) lights are popular choices, each with specific characteristics that can support different aspects of the growth cycle. Knowing how to manipulate these cycles and types of light will allow you to optimize the production and quality of the cannabis grown.
2. What is the Ideal Light Cycle for Cannabis Plant Growth?
The light cycle is one of the most critical factors in the growth of cannabis plants. Depending on the growth stage the plant is in, a specific light cycle is recommended to maximize its development. Generally, three main stages can be identified: germination, vegetative , and flowering.
Stages and Cycles of Light
- Germination: At this stage, newly sown cuttings or seeds should receive approximately 18 hours of light per day, which stimulates their initial development.
- Vegetative Stage: During this phase, which lasts for several weeks, it is advisable to provide a cycle of 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness. This regime favors the growth and strengthening of the plant.
- Flowering Stage: When this phase is reached, the optimal cycle changes to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This reduction in light induces the flowering process and cannabinoid production.
It is essential to maintain a controlled environment during cannabis cultivation, ensuring that the hours of light are accurate and that the quality of the light is adequate. Specialized grow lights, such as LEDs and metal halides, are recommended to provide the proper spectrum that plants need at each stage. Assessing temperature and humidity is also essential to optimize the photosynthesis process and the overall well-being of plants.
3. How to Adjust Your Light Cycle During Different Phases of Growth
The light cycle is a crucial factor in cannabis cultivation, as it directly influences the growth and development of the plant. Properly adjusting the hours of light during the different phases of growth is essential to maximize the potential of your crop. In general, cannabis plants have three main phases: the seedling stage, the vegetative stage, and the flowering stage.
Seedling Stage
During the seedling stage, which lasts approximately 2 to 4 weeks, it is advisable to maintain a light cycle of 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness. This cycle helps young plants establish strong, healthy roots, as well as encouraging robust and vigorous growth.
Vegetative Phase
In the vegetative stage, which can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months, it is suggested to stick with an 18/6 or even 20/4 cycle to maximize vegetative growth. During this phase, plants focus on developing leaves and structure, which is vital for future flower production.
Flowering Phase
Finally, when starting the flowering phase, it is necessary to change the cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This transition is key to stimulating flower and resin production in cannabis plants. It is important to ensure that during the 12 hours of darkness there are no interruptions in light, as this could negatively affect the formation of the buds.
4. Practical Tips for Handling Blackout Emergencies in the Crop
Blackouts can seriously impact cannabis cultivation, especially if they occur during critical periods such as the flowering phase. Here are some practical tips to minimize damage and maintain the health of your plants in these unforeseen situations.
1. Maintain a Backup System
A backup power generator is essential. Make sure it’s powerful enough to power your lights and ventilation systems. You can also consider a backup battery for automatic irrigation systems.
2. Temperature and Humidity Control
- Passive Ventilation: Open windows and doors to facilitate air circulation.
- Use of Portable Fans: Have battery-powered fans available to maintain consistent airflow.
- Monitoring: Use thermometers and hygrometers to monitor environmental conditions.
3. Plant Protection
When a power outage is expected, consider covering your plants with thermal blankets or reflective materials to protect them from the cold or excessive heat. This can also help decrease temperature fluctuation.
Remember that pre-planning and preparation are key. Maintaining an adequate inventory of equipment and supplies can make all the difference in the success of your grow during a blackout.
5. Essential Backup Equipment to Minimize the Impact of a Power Failure
A power outage can be disastrous for any cannabis grower, especially if you’re growing indoors. To ensure that your grow progresses smoothly, it’s crucial to have backup equipment that supports plant growth. Below are some of the essential pieces of equipment you should consider to protect your crop.
1. Combustion Generators
Combustion generators are an effective option for keeping your lighting and ventilation system running. There are models that run on gasoline, diesel, or propane gas. Make sure you choose a generator that has enough power to cover the energy demand of your crop.
2. Battery Systems and Inverters
Another key component is battery and inverter systems. These systems allow energy to be stored during daylight hours and released in the event of a power outage. Inverters convert battery power into alternating current, providing a reliable option for operating your electrical equipment.
3. Emergency Lighting Systems
- Portable LED Lamps
- Solar Lights
- Energy-efficient lighting
Installing emergency lighting systems can be a great way to ensure that your plants continue to receive light in the event of a power outage. These options are ideal for their low energy consumption and easy installation.